What Industries Are Included in the Application Scenarios of How to Wire Resistors?
I. Introduction
Resistors are fundamental components in electrical circuits, serving the crucial role of controlling the flow of electric current. By providing resistance, they help to manage voltage levels, protect sensitive components, and ensure the proper functioning of electronic devices. The importance of resistors cannot be overstated, as they are integral to a wide range of applications across various industries. This blog post will explore the diverse application scenarios of resistors, highlighting their significance in consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, medical devices, industrial automation, renewable energy, and home appliances.
II. Understanding Resistors
A. Types of Resistors
Resistors come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
1. **Fixed Resistors**: These resistors have a constant resistance value and are commonly used in circuits where a specific resistance is required.
2. **Variable Resistors (Potentiometers)**: These allow for adjustable resistance, making them ideal for applications such as volume controls in audio equipment.
3. **Specialty Resistors**: This category includes thermistors, which change resistance with temperature, and photoresistors, which vary resistance based on light exposure.
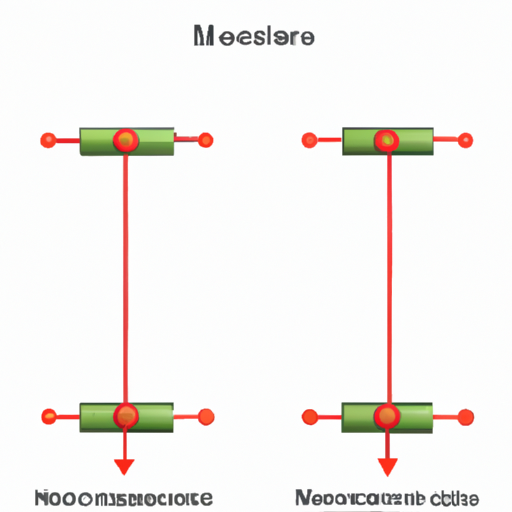
B. Basic Principles of Wiring Resistors
Understanding how to wire resistors is essential for their effective application.
1. **Series and Parallel Configurations**: Resistors can be wired in series, where the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, or in parallel, where the total resistance decreases.
2. **Ohm’s Law and Resistance Calculation**: Ohm’s Law (V = IR) is fundamental in calculating voltage, current, and resistance in circuits, guiding the proper wiring of resistors.
III. Application Scenarios of Resistors
A. Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, resistors play a vital role in circuit boards. They are used in devices such as televisions, smartphones, and laptops to manage current flow and protect sensitive components. For instance, in smartphones, resistors help regulate power to the display and touch sensors, ensuring optimal performance.
B. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on resistors, particularly in Engine Control Units (ECUs). These units use resistors to process signals from various sensors, enabling efficient engine management. Additionally, resistors are crucial in safety systems like Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) and airbags, where they help control the deployment of safety features.
C. Telecommunications
In telecommunications, resistors are essential for signal conditioning and amplification. They are used in networking equipment, such as routers and switches, to ensure that signals are transmitted accurately and efficiently. Proper wiring of resistors in these devices is critical for maintaining signal integrity and preventing data loss.
D. Medical Devices
Resistors are indispensable in the medical field, particularly in diagnostic equipment and patient monitoring systems. For example, in electrocardiograms (ECGs), resistors help filter and amplify the electrical signals generated by the heart, providing accurate readings for healthcare professionals. The reliability of these devices is paramount, making the proper application of resistors crucial.
E. Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, resistors are integral to control systems that manage machinery and robotics. They help regulate current and voltage levels, ensuring that equipment operates safely and efficiently. For instance, in robotic arms, resistors are used in feedback loops to maintain precise control over movement and positioning.
F. Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector also benefits from the application of resistors. In solar inverters, resistors are used to manage the conversion of solar energy into usable electricity. Similarly, in wind turbines, resistors play a role in controlling the electrical output and ensuring the stability of the system.
G. Home Appliances
In home appliances, resistors are commonly found in heating elements and control circuits for smart appliances. For example, in electric kettles, resistors help regulate the temperature, ensuring that water is heated efficiently. In smart appliances, resistors are used in control circuits to enable features like remote operation and energy monitoring.
IV. Wiring Techniques for Resistors
A. Best Practices for Wiring Resistors
When wiring resistors, adhering to best practices is essential for optimal performance:
1. **Ensuring Proper Ratings and Tolerances**: It is crucial to select resistors with appropriate ratings for voltage and power to prevent overheating and failure.
2. **Heat Management Considerations**: Resistors generate heat during operation, so proper heat dissipation techniques, such as using heat sinks or ensuring adequate airflow, are vital.
B. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to issues in resistor applications:
1. **Incorrect Configuration**: Wiring resistors in the wrong configuration (series vs. parallel) can lead to unexpected resistance values and circuit malfunctions.
2. **Overheating and Component Failure**: Failing to account for power ratings can result in overheating, damaging the resistor and potentially other components in the circuit.
V. Future Trends in Resistor Applications
A. Advancements in Resistor Technology
The future of resistor applications is promising, with advancements in technology paving the way for new possibilities:
1. **Smart Resistors and IoT Integration**: The integration of resistors with Internet of Things (IoT) technology is on the rise, enabling smarter devices that can adapt to user needs and environmental conditions.
2. **Miniaturization and Enhanced Performance**: As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, the demand for miniaturized resistors with enhanced performance characteristics is increasing.
B. Emerging Industries and Applications
New industries are emerging that will further expand the application of resistors:
1. **Electric Vehicles**: As the automotive industry shifts towards electric vehicles, resistors will play a critical role in battery management systems and power electronics.
2. **Wearable Technology**: The rise of wearable devices will necessitate the use of compact, efficient resistors to ensure accurate monitoring and data collection.
VI. Conclusion
In summary, resistors are indispensable components across a multitude of industries, from consumer electronics to renewable energy. Their ability to control current and voltage makes them essential for the proper functioning of various devices and systems. As technology continues to evolve, the applications of resistors will expand, leading to innovative solutions and improved performance in countless fields. The future of resistor applications is bright, and further exploration and learning in this area will undoubtedly yield exciting developments.
VII. References
- Academic Journals
- Industry Reports
- Technical Manuals and Guides
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the industries that utilize resistors and the various application scenarios in which they are wired. By understanding the importance of resistors and their wiring techniques, readers can appreciate their role in modern technology and the future trends shaping their applications.