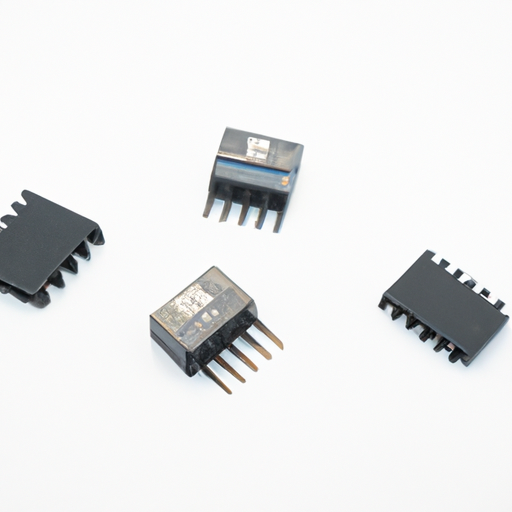
Important Product Categories of Precision Resistors
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Precision Resistors
Precision resistors are electronic components designed to provide accurate and stable resistance values. Unlike standard resistors, which may have a wide tolerance range, precision resistors are manufactured to meet stringent specifications, ensuring minimal deviation from their stated resistance values. This accuracy is crucial in applications where even slight variations can lead to significant performance issues.
B. Importance of Precision Resistors in Electronic Applications
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, precision is paramount. From medical devices that monitor vital signs to automotive systems that ensure safety, precision resistors play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of electronic circuits. Their ability to deliver consistent performance under varying conditions makes them indispensable in high-stakes environments.
C. Overview of the Article
This article will explore the various types of precision resistors, their key specifications, applications across different industries, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of these essential components.
II. Types of Precision Resistors
A. Thin Film Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Thin film resistors are created by depositing a thin layer of resistive material onto a substrate, typically using techniques such as sputtering or evaporation. This process allows for precise control over the thickness and composition of the film, resulting in highly accurate resistance values.
2. Characteristics and Applications
Thin film resistors are known for their low noise, high stability, and excellent temperature coefficients. They are commonly used in applications requiring high precision, such as instrumentation, medical devices, and aerospace systems.
B. Thick Film Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Thick film resistors are produced by screen printing a paste of resistive material onto a ceramic substrate and then firing it at high temperatures. This method allows for the creation of resistors with a wide range of resistance values and power ratings.
2. Characteristics and Applications
Thick film resistors are robust and can handle higher power levels compared to thin film resistors. They are often used in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and industrial equipment where durability is essential.
C. Wirewound Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Wirewound resistors are made by winding a metal wire, typically made of nickel-chromium or copper-nickel alloy, around a ceramic or fiberglass core. The resistance value is determined by the wire's length, diameter, and material.
2. Characteristics and Applications
Wirewound resistors offer excellent power handling capabilities and are known for their high precision and stability. They are commonly used in power supplies, audio equipment, and precision measurement devices.
D. Foil Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Foil resistors are manufactured by etching a thin metallic foil into a specific pattern to create the desired resistance. This process allows for exceptional precision and stability.
2. Characteristics and Applications
Foil resistors are renowned for their low temperature coefficients and high accuracy, making them ideal for applications in metrology, aerospace, and high-end audio equipment.
E. Metal Film Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Metal film resistors are produced by depositing a thin layer of metal onto a ceramic substrate and then trimming the film to achieve the desired resistance value. This process allows for tight tolerances and excellent performance.
2. Characteristics and Applications
Metal film resistors are widely used in precision applications due to their low noise and high stability. They are commonly found in instrumentation, telecommunications, and high-frequency circuits.
III. Key Specifications of Precision Resistors
A. Tolerance
1. Definition and Importance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from the nominal resistance value. In precision resistors, lower tolerance levels indicate higher accuracy, which is crucial in applications where precision is vital.
2. Common Tolerance Levels
Precision resistors typically have tolerance levels ranging from ±0.01% to ±1%, with lower values being preferred in high-precision applications.
B. Temperature Coefficient
1. Definition and Importance
The temperature coefficient indicates how much a resistor's value changes with temperature. A low temperature coefficient is essential for maintaining accuracy in varying environmental conditions.
2. Impact on Performance
Precision resistors with low temperature coefficients ensure stable performance across a wide temperature range, making them suitable for critical applications in aerospace and medical devices.
C. Power Rating
1. Definition and Importance
Power rating refers to the maximum power a resistor can dissipate without overheating. It is a crucial specification that determines the resistor's suitability for specific applications.
2. Applications Based on Power Rating
High-power precision resistors are used in applications such as power supplies and motor control, while lower power ratings are sufficient for signal processing and low-power electronics.
D. Voltage Rating
1. Definition and Importance
Voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage a resistor can handle without breaking down. This specification is vital for ensuring the reliability and safety of electronic circuits.
2. Applications Based on Voltage Rating
Precision resistors with high voltage ratings are essential in applications such as telecommunications and industrial automation, where high voltages are common.
IV. Applications of Precision Resistors
A. Medical Devices
1. Importance of Accuracy and Reliability
In medical devices, precision resistors are critical for ensuring accurate measurements and reliable performance. Any deviation can lead to incorrect diagnoses or treatment.
2. Examples of Use
Precision resistors are used in devices such as ECG machines, blood pressure monitors, and infusion pumps, where accuracy is paramount.
B. Automotive Industry
1. Role in Safety and Performance
Precision resistors play a vital role in automotive systems, contributing to safety features and overall vehicle performance.
2. Examples of Use
They are used in anti-lock braking systems (ABS), engine control units (ECUs), and sensor applications, where precise measurements are essential for optimal functioning.
C. Telecommunications
1. Importance in Signal Integrity
In telecommunications, maintaining signal integrity is crucial for effective communication. Precision resistors help minimize signal distortion and loss.
2. Examples of Use
They are commonly found in RF amplifiers, signal processing circuits, and network equipment, ensuring reliable data transmission.
D. Aerospace and Defense
1. Critical Applications and Standards
In aerospace and defense, precision resistors must meet stringent standards for reliability and performance, as failures can have catastrophic consequences.
2. Examples of Use
They are used in navigation systems, radar equipment, and communication devices, where precision is non-negotiable.
E. Consumer Electronics
1. Importance in Everyday Devices
Precision resistors are also found in consumer electronics, contributing to the performance and reliability of everyday devices.
2. Examples of Use
They are used in smartphones, televisions, and audio equipment, where high-quality performance is expected by consumers.
V. Emerging Trends in Precision Resistors
A. Miniaturization and Integration
As electronic devices become smaller and more compact, there is a growing demand for miniaturized precision resistors that can fit into tight spaces without compromising performance.
B. Advancements in Materials and Technology
Innovations in materials science are leading to the development of new resistor types with improved performance characteristics, such as lower noise and better thermal stability.
C. Increased Demand for High-Performance Resistors
With the rise of high-performance applications, there is a growing need for precision resistors that can handle extreme conditions and deliver consistent results.
D. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
As industries move towards more sustainable practices, manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and production methods for precision resistors, reducing their environmental impact.
VI. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
Precision resistors are essential components in modern electronics, offering high accuracy, stability, and reliability across various applications. Understanding the different types, specifications, and applications of precision resistors is crucial for engineers and designers in the field.
B. Future Outlook for Precision Resistors
The future of precision resistors looks promising, with advancements in technology and materials driving innovation. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-performance precision resistors will only increase.
C. Final Thoughts on the Importance of Precision Resistors in Modern Technology
In a world where precision is paramount, the role of precision resistors cannot be overstated. They are the unsung heroes of electronic circuits, ensuring that devices function accurately and reliably, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for users across the globe.
VII. References
A. Academic Journals
- IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology
- Journal of Electronic Materials
B. Industry Reports
- Market Research Reports on Resistor Technologies
- Industry Analysis on Precision Resistors
C. Manufacturer Specifications and Data Sheets
- Manufacturer websites and product catalogs
- Technical data sheets from leading resistor manufacturers
This comprehensive overview of precision resistors highlights their importance in various applications and the trends shaping their future. As technology continues to advance, precision resistors will remain a critical component in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of electronic devices.